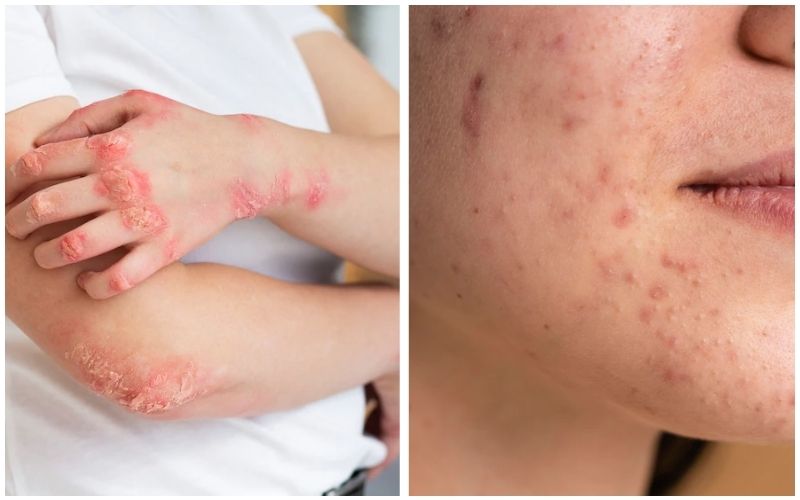
Psoriasis and eczema are prevalent skin conditions, but they can sometimes be difficult to distinguish. No matter the type of symptoms you face, consult with your dermatologist at the earliest to get the appropriate diagnosis. Once you know which condition you have, you can treat it appropriately.
Knowing the difference between psoriasis and eczema can help you identify what’s going on with your skin to get the proper treatment. So, this article will teach you about the two most common inflammatory skin conditions: eczema and psoriasis. We’ll discuss the symptoms, causes, and treatment options of both.
What are psoriasis and eczema?
Psoriasis is a common skin condition characterised by thick, red skin patches. Doctors aren’t sure what causes people to develop psoriasis; they suspect that genetic factors and environmental triggers may play a role.
Eczema, another autoimmune condition that can also present itself on the skin, also presents similar symptoms as psoriasis; it is often triggered by allergens or irritants such as tree pollen or strong soaps. When someone suffering from eczema comes in contact with something they’re sensitive to—like tree pollen or strong soaps—the immune system produces an allergic reaction, and inflammation occurs.
Psoriasis vs Eczema Symptoms
Psoriasis and eczema can appear similar, but there are differences between the two. Therefore, it’s essential to identify which one you have to treat correctly.
Psoriasis
1. Plaque psoriasis- Plaque psoriasis causes red patches of dry skin with a silvery scale on the elbows, knees, and back. When the patches appear on your head, doctors call it scalp psoriasis.
2. Nail psoriasis in the fingernails and toenails can cause pitting, discolouration, or weird growth patterns. If a person has severe psoriasis, their nails may become loose, can separate from the nail beds, or might even crumble.
3. Inverse psoriasis- Inverse psoriasis develops on the skin in places where the body tends to sweat, including the groin and under the buttocks. It can also appear on your breasts and between the folds of skin. This form of psoriasis looks different from plaque psoriasis—inverse psoriasis causes red patches of skin, but they are smooth, not scaly.
4. Psoriatic arthritis- Psoriasis can cause your joints to ache as severely as they do when you have arthritis. Some people with psoriatic arthritis feel joint pain even though they don’t have any red, scaly skin or other psoriasis symptoms.
Eczema
1. Atopic dermatitis- More than 26 million people have atopic dermatitis—also known as eczema—including more than 9 million babies and young children. Those with atopic dermatitis often experience itchy, dry skin that can cause red or brown discolouration patches.
2. Contact dermatitis- People with contact dermatitis develop an itchy, burning, or blistering skin reaction when they touch something that irritates them or causes an allergic reaction. This condition can be tough to live with if left untreated.
3. Neuro dermatitis- Those who suffer from neurodermatitis experience itchy, scaly patches on their necks and limbs. A flare-up of symptoms can occur whenever stress, anxiety, or environmental irritants cause the patient’s immune system to overreact.
4. Sebhorreic dermatitis- People with seborrheic dermatitis develop dry, itchy patches on their scalp and sometimes on the sides of their nose and face. It often affects people with oily skin or weak immune systems.
5. Statis dermatitis- Stasis dermatitis makes your lower legs get itchy, discoloured, and have open sores. It’s caused by blood not flowing right to your legs, so they don’t get enough oxygen.
Psoriasis vs Eczema Causes
Psoriasis
When it comes to psoriasis, genetics is a significant factor. People with a family history of psoriasis are more likely to develop it themselves and develop symptoms earlier. In addition, stress can trigger psoriasis symptoms in those with the condition. People living with Psoriasis also experience periods of remission and exacerbation related to stress levels or exposure to triggering substances.
Eczema
People with eczema have a genetic predisposition to the condition, but many other factors determine whether or not they’ll develop it. For example, some people with eczema have a gene mutation that makes their skin more vulnerable to damage and infection; others develop it due to exposure to irritants, allergens, or other triggers.
Psoriasis vs Eczema Treatment
Psoriasis treatment
Doctors may recommend creams or ointments that contain steroids or unique ultraviolet light treatments for people with psoriasis. Doctors may also prescribe oral drugs for people who do not respond to topical medications or light therapy.
Eczema treatment
Doctors may recommend that people with psoriasis bathe regularly and apply moisturiser to their dry skin. Patients can also use over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms, including dandruff shampoos and lotions. In addition, some people may benefit from light therapy, an alternative treatment that exposes the skin to ultraviolet rays. Prescription creams and ointments are available through a doctor’s prescription and oral medications. Injectable medications may be used as well.
So, this was all about the differences between psoriasis and eczema. Hope you will find this article helpful. Also, if you are looking for excellent pharmaceutical care products and services, you can visit Flinders Discount Chemist.